[TOC]
三、JS中异步方法
1. setTimeout、setInterval
setTimeout()方法设置一个定时器,该定时器在定时器到期后执行一个函数或指定的一段代码。
setInterval() 方法重复调用一个函数或执行一个代码段,在每次调用之间具有固定的时间延迟。
setTimeout的用法(setInterval用法一样):
function f() { console.log('f') }
function t(a) { console.log(a) }
setTimeout(f, 0);
setTimeout(f, 1000);
setTimeout(t, 0, 'hello');
var id = setTimeout(t, 1000, '我不会被执行');
setTimeout("console.log('类似evel方法')"); // nodejs中此处会报错
clearTimeout(id) // 取消了setTimeout函数的回调
// setInterval()例子,执行了5次函数
var i = 0;
function fn(a) {
console.log(a); console.log(i);
i++;
if (i > 5) {
// 清除setInterval执行
clearInterval(id)
}
}
var id = setInterval (fn, 1000, 'hello');
参数(setTimeout、setInterval一样):
第一个参数(必填):带执行的函数,也可以使用字符串代替函数,在
delay毫秒之后执行字符串 (使用该语法是不推荐的, 原因和使用eval一样,有安全风险)第二个参数(可选):延迟的毫秒数 (一秒等于1000毫秒),函数的调用会在该延迟之后发生。如果省略该参数,delay取默认值0。实际的延迟时间可能会比 delay 值长
第三个以后的参数(可选):执行函数的参数
返回值
返回一个正整数,表示定时器的编号。
这个值传递给
clearTimeout()可以用来来取消setTimeout的定时。这个值传递给
clearInterval()可以用来来取消setInterval的定时。
注意:IE9 及更早的 IE 浏览器不支持向延迟函数传递额外参数的功能。
1.1 关于延迟
https://html.spec.whatwg.org/multipage/timers-and-user-prompts.html#timers
目前看到的文档关于setTimeout第二个参数的说明:
If timeout is less than 0, then set timeout to 0.
If nesting level is greater than 5, and timeout is less than 4, then set timeout to 4.
翻译成中文:
如果timeout小于0,则将timeout设置为0。
如果嵌套级别大于5,并且超时小于4,则将超时设置为4。
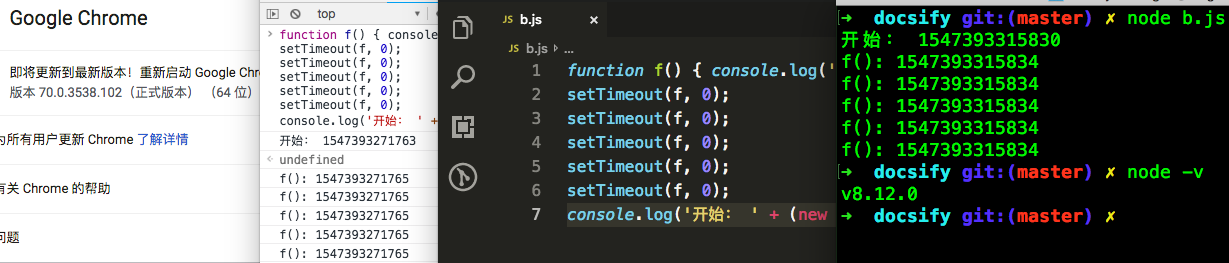
1、如果JavaScript中没有耗时久的代码,并且setTimeout函数延迟是0的话,那么在浏览器中和nodejs中都是会立刻就执行的:
function f() { console.log('f(): ' + (new Date()).getTime()) }
setTimeout(f, 0);
setTimeout(f, 0);
setTimeout(f, 0);
setTimeout(f, 0);
setTimeout(f, 0);
console.log('开始: ' + (new Date()).getTime());
下面的图片分别是在浏览器中和nodejs中的输出结果。
2、如果JavaScript同步代码有耗时的代码,那么setTimeout回调函数执行的时间就会大于设置的时间:
function f() { console.log('f(): ' + (new Date()).getTime()) }
setTimeout(f, 0);
var t = (new Date()).getTime()
console.log('开始: ' + t);
while(true){
if (t < (new Date()).getTime() - 3000) {
break;
}
}
// 输出结果
// 开始: 1547394071675
// f(): 1547394074677
可以看到上面的setTimeout回调函数要在3秒以后才能执行
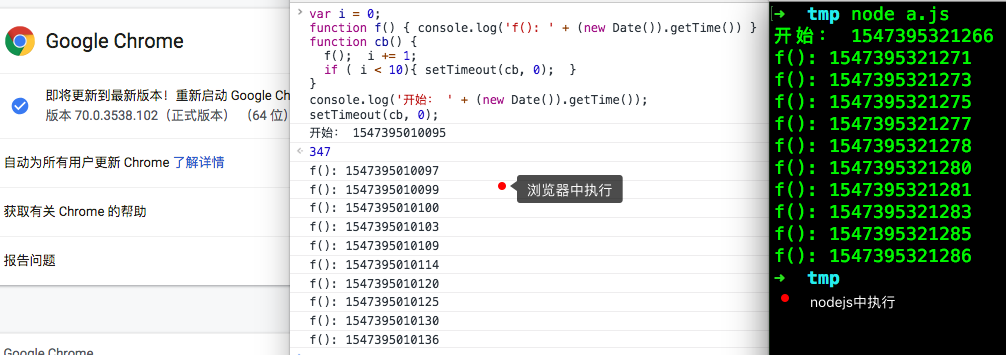
3、如果setTimeout有超过5层以上的嵌套
var i = 0;
function f() { console.log('f(): ' + (new Date()).getTime()) }
function cb() {
f(); i += 1;
if ( i < 10){ setTimeout(cb, 0); }
}
console.log('开始: ' + (new Date()).getTime());
setTimeout(cb, 0);
通过实际运行结果可以看见,在浏览器中第五次以后执行会大于4毫秒。
nodejs是最少间隔1毫秒执行一次。
2. setImmediate()
此方法是一个特殊timer,目前在nodejs得到支持,在浏览器环境还没有成为标准,在Google浏览器(70版本)中还不支持,
在nodejs中etImmediate()是放在check阶段执行的
setImmediate(function(a, b) {
console.log('setImmediate:'+ a + b)
}, 5000, 'hello')
// setImmediate:5000hello
***注意:***setImmediate不能设置延迟时间,setImmediate第一个参数是回调函数,后面的参数是回调函数的参数。
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('setTimeout')
}, 0)
setImmediate(function() {
console.log('setImmediate')
})
setTimeout和setImmediate在nodejs有时输出顺序不一致。
setTimeout与setImmediate先后入队之后,首先进入的是timers阶段,如果我们的机器性能一般或者加入了一个同步长耗时操作,那么进入timers阶段,1ms已经过去了,那么setTimeout的回调会首先执行。
如果没有到1ms,那么在timers阶段的时候,超时时间没到,setTimeout回调不执行,事件循环来到了poll阶段,这个时候队列为空,此时有代码被setImmediate(),于是先执行了setImmediate()的回调函数,之后在下一个事件循环再执行setTimemout的回调函数。
3. process.nextTick()
process.nextTick()方法目前只在nodejs中支持。
有时我们想要立即异步执行一个任务,可能会使用延时为0的定时器,但是这样开销很大。我们可以换而使用process.nextTick(),它会将传入的回调放入nextTickQueue队列中,不管事件循环进行到什么地步,都在当前执行栈的操作结束的时候调用。这点很重要,注意。
process.nextTick方法指定的回调函数,总是在当前执行队列的尾部触发,多个process.nextTick语句总是一次执行完(不管它们是否嵌套),递归调用process.nextTick,将会没完没了,主线程根本不会去读取事件队列,导致阻塞后续调用,直至达到最大调用限制。
相比于在定时器中采用红黑树树的操作时间复杂度为0(lg(n)),而process.nextTick()的时间复杂度为0(1),相比之下更高效。
一个例子:
setTimeout(() => { // settimeout1
process.nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick1')) // nextTick1
setTimeout(() => { // settimeout2
console.log('setTimout1')
process.nextTick(() => { // nextTick2
console.log('nextTick2')
setImmediate(() => console.log('setImmediate1')) // check2
process.nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick3')) // nextTick4
})
setImmediate(() => console.log('setImmediate2')) // check1
process.nextTick(() => console.log('nextTick4')) // nextTick3
console.log('sync2')
setTimeout(() => console.log('setTimout2'), 0) // settimeout3
}, 0)
console.log('sync1')
}, 0)
// sync1 nextTick1 setTimout1 sync2 nextTick2 nextTick4 nextTick3 setImmediate2 setImmediate1 setTimout2
上面的代码执行过程:
- node初始化
- 执行JavaScript代码
- 遇到
setTimeout, 把回调函数放到Timer队列中,记为settimeout1
- 遇到
- 没有
process.nextTick回调,略过 - 没有微任务,略过
- 执行JavaScript代码
- 进入第一次事件循环
- 进入timer阶段
- 检查Timer队列是否有可执行的回调,此时队列有一个回调:settimeout1
- 执行settimeout1回调:
- 遇到process.nextTick,把回调加入到nextTick队列,记为nextTick1
- 遇到setTimeout,把回调加入到Timer队列,记为settimeout2
- 遇到console,输出:sync1
- 检查
process.nextTick队列,发现有一个回调nextTick1,执行,输出:nextTick1 - 检查微任务队列,没有略过
- Timer阶段执行结束,此阶段输出:
sync1 nextTick1
- Pending I/O Callback阶段没有任务,略过
- 进入 Poll 阶段
- 检查是否存在尚未完成的回调,此时有一个Timer回调待执行:settimeout2
- 执行settimeout2回调
- 遇到console,输出:setTimout1
- 遇到process.nextTick,把回调加入到nextTick队列,记为nextTick2
- 遇到setImmediate,把回调加入到Check队列,记为check1
- 遇到process.nextTick,把回调加入到nextTick队列,记为nextTick3
- 遇到console,输出:sync2
- 遇到setTimeout,把回调加入到Timer队列,记为settimeout3
- 检查
process.nextTick队列,发现有两个回调:nextTick2,nextTick3- 执行nextTick2
- 遇到console,输出:nextTick2
- 遇到setImmediate,把回调加入到Check队列,记为check2
- 遇到process.nextTick,把回调加入到nextTick队列,记为nextTick4
- 执行nextTick3,输出:nextTick4
- 由于又加了nextTick4,在nextTick队列后面执行,输出:nextTick3
- 执行nextTick2
- 检查微任务队列,没有略过
- Poll 阶段执行结束,此阶段输出:
setTimout1 sync2 nextTick2 nextTick4 nextTick3
- 进入check 阶段
- 检查check队列是否有可执行的回调,此时队列有两个回调:check1、check2
- 执行check1回调,输出:setImmediate2
- 执行check2回调,输出:setImmediate1
- check 阶段执行结束,此阶段输出:
setImmediate2 setImmediate1
- closing阶段没有任务,略过
- 检查是否还有活跃的
handles(定时器、IO等事件句柄),有,继续下一轮事件循环
- 进入timer阶段
- 进入第二次事件循环
- 进入Timer阶段
- 检查Timer队列是否有可执行的回调,此时队列有一个回调:settimeout3
- 执行settimeout3回调,输出:setTimout2
- Pending I/O Callback、Poll、check、closing阶段没有任务,略过
- 检查是否还有活跃的
handles(定时器、IO等事件句柄),没有了,结束事件循环,退出程序
- 进入Timer阶段
- 程序执行结束,输出结果:
sync1 nextTick1 setTimout1 sync2 nextTick2 nextTick4 nextTick3 setImmediate2 setImmediate1 setTimout2
参考资料
https://html.spec.whatwg.org/multipage/timers-and-user-prompts.html#timers
