[TOC]
vue3的路由vue-router4.x.x
在Vue 3中,需要使用vue-router的4.x.x版本。Vue 3与Vue 2在路由方面不兼容,因此从Vue 2迁移到Vue 3时,需要使用vue-router的4.x.x版本。
vue-router 4.x.x版本的主要变化:
- API大部分保持不变:从Vue Router 3到4,大部分API没有变化,这使得迁移相对容易1。
- 更灵活的历史模式配置:新的历史模式配置更加灵活,替代了旧的mode配置
1. 对路由的理解
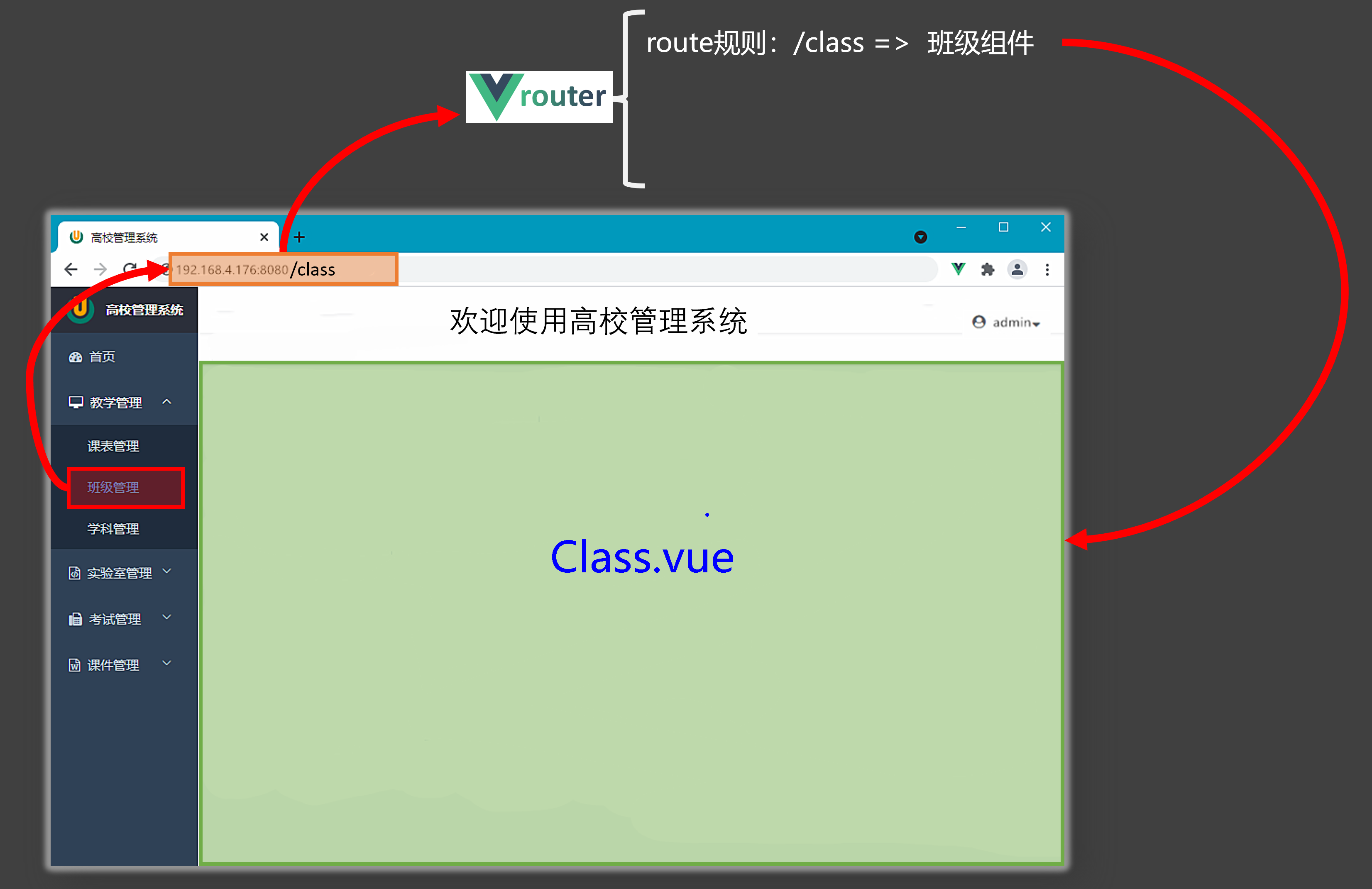
1.1 使用路由代码示例
路由配置文件代码如下:
import {createRouter,createWebHistory} from 'vue-router'
import Home from '@/pages/Home.vue'
import About from '@/pages/About.vue'
const router = createRouter({
history:createWebHistory(),
routes:[
{ path:'/home', component:Home },
{ path:'/about', component:About }
]
})
export default router
main.ts代码如下:
import router from './router/index'
app.use(router)
app.mount('#app')
App.vue代码如下:
<template>
<div class="app">
<h2 class="title">Vue路由测试</h2>
<!-- 导航区 -->
<div class="navigate">
<RouterLink to="/home" active-class="active">首页</RouterLink>
<RouterLink to="/about" active-class="active">关于</RouterLink>
</div>
<!-- 展示区 -->
<div class="main-content">
<RouterView></RouterView>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup name="App">
import {RouterLink,RouterView} from 'vue-router'
</script>
1.2 两个注意点
- 1、路由组件通常存放在
pages或views文件夹,一般组件通常存放在components文件夹。 - 2、通过点击导航,视觉效果上“消失” 了的路由组件,默认是被卸载掉的,需要的时候再去挂载。
2. 路由配置项说明
2.1 路由器工作模式
history模式优点:
URL更加美观,不带有#,更接近传统的网站URL。
缺点:后期项目上线,需要服务端配合处理路径问题,否则刷新会有404错误。const router = createRouter({ history:createWebHistory(), //history模式 /******/ })hash模式优点:兼容性更好,因为不需要服务器端处理路径。
缺点:URL带有#不太美观,且在SEO优化方面相对较差。const router = createRouter({ history:createWebHashHistory(), //hash模式 /******/ })
2.2 命名路由
作用:可以简化路由跳转及传参(后面就讲)。
给路由规则命名:
routes:[
{ name:'zhuye', path:'/home', component:Home },
{ name:'xinwen', path:'/news', component:News, },
{ name:'guanyu', path:'/about', component:About }
]
使用路由名字跳转:
<!--简化前:需要写完整的路径(to的字符串写法) -->
<router-link to="/news/detail">跳转</router-link>
<!--简化后:直接通过名字跳转(to的对象写法配合name属性) -->
<router-link :to="{name:'guanyu'}">跳转</router-link>
2.3 嵌套路由
1、配置路由规则,使用children配置项:
const router = createRouter({
history:createWebHistory(),
routes:[
{
name:'xinwen',
path:'/news',
component:News,
children:[
{ name:'xiang', path:'detail', component:Detail }
]
},
]
})
export default router
2、跳转路由(记得要加完整路径):
<router-link to="/news/detail">xxxx</router-link>
<!-- 或 -->
<router-link :to="{path:'/news/detail'}">xxxx</router-link>
3、记得去Home组件中预留一个<router-view>
<template>
<div class="news">
<nav class="news-list">
<RouterLink v-for="news in newsList" :key="news.id" :to="{path:'/news/detail'}">
{{news.name}}
</RouterLink>
</nav>
<div class="news-detail">
<RouterView/>
</div>
</div>
</template>
2.4 props 配置
作用:让路由组件更方便的收到参数(可以将路由参数作为props传给组件)
{
name:'xiang',
path:'detail/:id/:title/:content',
component:Detail,
// props的对象写法,作用:把对象中的每一组key-value作为props传给Detail组件
// props:{a:1,b:2,c:3},
// props的布尔值写法,作用:把收到了每一组params参数,作为props传给Detail组件
// props:true
// props的函数写法,作用:把返回的对象中每一组key-value作为props传给Detail组件
props(route){
return route.query
}
}
2.5 重定向redirect
作用:将特定的路径,重新定向到已有路由。
具体编码:
{ path:'/', redirect:'/about' }
3. router-link说明
3.1 to的两种写法
<!-- 第一种:to的字符串写法 -->
<router-link active-class="active" to="/home">主页</router-link>
<!-- 第二种:to的对象写法 -->
<router-link active-class="active" :to="{path:'/home'}">Home</router-link>
3.4 replace属性
作用:控制路由跳转时操作浏览器历史记录的模式。
浏览器的历史记录有两种写入方式:分别为
push和replace:push是追加历史记录(默认值)。replace是替换当前记录。
开启
replace模式:<RouterLink replace .......>News</RouterLink>
4. 路由传参
4.1 query参数
路由文件:
// router/index.js
import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from 'vue-router';
import Home from '../views/Home.vue';
import Detail from '../views/Detail.vue';
const routes = [
{ path: '/', name: 'Home', component: Home },
{ path: '/detail', name: 'Detail', component: Detail }
];
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(),
routes
});
export default router;
1、template 模板中使用 RouterLink 方式传递参数
<!-- 跳转并携带query参数(to的字符串写法) -->
<router-link to="/detail?a=1&b=2&content=欢迎你">跳转</router-link>
<!-- 跳转并携带query参数(to的对象写法): 使用path -->
<router-link :to="{ path: '/detail', query: { name: 'Alice', age: 25 } }">
跳转
</router-link>
<!-- 跳转并携带query参数(to的对象写法): 使用name -->
<router-link :to="{ name:'Detail', query: { name: 'Alice', age: 25 } }">
跳转
</router-link>
2、JS 代码中使用 router.push 传递参数
<template>
<div>
<button @click="goToDetail">Go to Detail</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useRouter } from 'vue-router';
const router = useRouter();
const goToDetail = () => {
// 使用 router.push 传递 query 参数
router.push({ name: 'Detail', query: { id: 2, name: 'another example' } });
};
</script>
3、在目标组件中获取 query 参数
<template>
<div>
<p>ID: {{ route.query.id }}</p>
<p>Name: {{ route.query.name }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useRoute } from 'vue-router';
const route = useRoute();
</script>
4.2 params参数
注意:
- 传递
params参数时,需要提前在路由配置中占位。 - 传递
params参数时,若使用to的对象写法,必须使用name配置项,不能用path。详情见8.2.1节的解释
路由文件:
// router/index.js
import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from 'vue-router';
import Home from '../views/Home.vue';
import Product from '../views/Product.vue';
const routes = [
{ path: '/', name: 'Home', component: Home },
{
path: '/product/:id/:name',
name: 'Product',
component: Product
}
];
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(),
routes
});
export default router;
在上述配置中,/product/:id/:name 定义了两个动态路由参数 id 和 name。
1、在模板中使用 RouterLink 传参
<template>
<div>
<h1>Home Page</h1>
<!-- 使用 RouterLink 传递多个 params 参数 -->
<RouterLink :to="{ name: 'Product', params: { id: 123, name: 'Smartphone' } }">
Go to Product Page
</RouterLink>
<!-- 跳转并携带params参数(to的字符串写法) -->
<RouterLink :to="`/product/123/Smartphone`">{{news.title}}</RouterLink>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { RouterLink } from 'vue-router';
</script>
2、JS 代码中使用 router.push 传递多个 params 参数
<template>
<div>
<button @click="goToProductPage">Go to Product Page</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useRouter } from 'vue-router';
const router = useRouter();
const goToProductPage = () => {
// 使用 router.push 传递多个 params 参数
router.push({ name: 'Product', params: { id: 456, name: 'Laptop' } });
};
</script>
3、在目标组件中获取 params 参数
<template>
<div>
<p>Product ID: {{ route.params.id }}</p>
<p>Product Name: {{ route.params.name }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useRoute } from 'vue-router';
const route = useRoute();
</script>
4.2.1 使用to的对象写法,必须使用name配置项的原因
是由于 路由匹配机制差异导致的:
基于路径(
path)匹配:Vue Router 的路由匹配是依据路径规则来进行的。当你使用params传参时,params参数会被嵌入到路径中。如果仅使用path而不使用name,在传递params参数时,需要手动把参数拼接到路径里,像这样:<template> <RouterLink :to="{ path: `/user/${userId}`, params: { userId: 123 } }">User Page</RouterLink> </template> <script setup> import { RouterLink } from 'vue-router'; const userId = 123; </script>基于名称(
name)匹配:使用name配置项时,Vue Router 会根据路由的名称来查找对应的路由配置。路由的名称是唯一的,通过名称来匹配路由更加简洁、直观,而且不需要手动拼接路径。
params 参数特性:
params依赖路由配置:params参数是和具体的路由配置紧密相关的,它们需要根据路由配置中的动态参数占位符来进行匹配。使用name可以确保params参数被正确地传递到对应的路由中。如果仅使用path而没有准确匹配路径中的参数占位符,可能会导致params参数无法正常传递。- 提高代码可维护性:在项目开发过程中,路由配置可能会发生变化,例如路径规则的修改。如果使用
name来进行路由跳转,即使路径规则改变,只要路由的名称不变,跳转代码就不需要修改,提高了代码的可维护性。
综上所述,在使用 params 传参且采用 to 的对象写法时,使用 name 配置项能让代码更简洁、直观,降低出错概率,提高代码的可维护性。
5. 编程式导航
路由组件的两个重要的属性:$route和$router变成了两个hooks
import {useRoute,useRouter} from 'vue-router'
const route = useRoute()
const router = useRouter()
// 获取路由参数
console.log(route.query)
console.log(route.parmas)
// 页面跳转方法
console.log(router.push)
console.log(router.replace)
// 路由跳转,并传参
router.push({ name: 'Product', params: { id: 456, name: 'Laptop' }
6. 导航守卫
正如其名,vue-router 提供的导航守卫主要用来通过跳转或取消的方式守卫导航。这里有很多方式植入路由导航中:全局的,单个路由独享的,或者组件级的。
6.1 全局守卫
Vue Router 4.x.x 提供了三种全局守卫:
beforeEach:在路由跳转前执行。beforeResolve:在导航被确认前执行。afterEach:在导航完成后执行。
注意事项:
next函数的弃用:在 Vue Router 4.x.x 中,next函数已被弃用,推荐使用return返回值来控制导航。- 异步操作:在守卫中执行异步操作时,确保使用
async/await或返回Promise。 - 性能优化:避免在全局守卫中执行耗时操作,以免影响路由跳转性能。
6.1.1 beforeEach
作用:在每次路由跳转前执行,常用于权限验证、路由拦截等。
参数:
to:目标路由对象(RouteLocationNormalized),包含目标路由的信息(如路径、参数、查询等)。from:当前路由对象(RouteLocationNormalized),包含当前路由的信息。next:控制路由跳转的函数(在 Vue Router 4.x.x 中,next函数已被弃用,推荐使用return返回值)。
返回值:
false:取消当前导航。RouteLocationRaw(如路径字符串或路由对象):重定向到指定路由。undefined或true:继续当前导航。
示例:
router.beforeEach((to, from) => { const isAuthenticated = checkAuth(); // 检查用户是否登录 if (to.meta.requiresAuth && !isAuthenticated) { return '/login'; // 重定向到登录页 // return { name: 'Login' }; } // 继续导航 }); // 支持 async 函数 router.beforeEach(async (to, from) => { const canAccess = await canUserAccess(to) // canUserAccess() 返回 `true` 或 `false` if (!canAccess) return '/login' })
6.1.2 beforeResolve
作用:在导航被确认前执行,通常用于确保异步操作(如数据加载)完成。
参数:
to:目标路由对象(RouteLocationNormalized)。from:当前路由对象(RouteLocationNormalized)。
返回值:
- 与
beforeEach相同。
- 与
示例:
router.beforeResolve(async (to, from) => { if (to.meta.requiresData) { try { await fetchData(); // 加载数据 } catch (error) { return '/error'; // 数据加载失败时重定向到错误页 } } // 继续导航 });
6.1.3 afterEach
作用:在导航完成后执行,通常用于日志记录、页面统计等。
参数:
to:目标路由对象(RouteLocationNormalized)。from:当前路由对象(RouteLocationNormalized)。
返回值:无。
示例:
router.afterEach((to, from) => { logPageView(to.path); // 记录页面访问 });
6.2 路由独享守卫:beforeEnter
在 Vue Router 4.x.x 中,路由独享守卫是直接定义在路由配置中的守卫,仅作用于该特定路由。它允许你在进入某个路由前执行特定的逻辑(如权限验证、数据加载等)。
作用:在进入特定路由前执行,常用于权限验证、数据加载等。
参数:
to:目标路由对象(RouteLocationNormalized),包含目标路由的信息(如路径、参数、查询等)。from:当前路由对象(RouteLocationNormalized),包含当前路由的信息。
返回值:
false:取消当前导航。RouteLocationRaw(如路径字符串或路由对象):重定向到指定路由。undefined或true:继续当前导航。
示例:
const routes = [ { path: '/admin', component: Admin, beforeEnter: (to, from) => { const isAdmin = checkAdmin(); // 检查用户是否是管理员 if (!isAdmin) { return '/unauthorized'; // 非管理员重定向到未授权页 } // 继续导航 } } ];路由独享守卫的执行顺序如下:
- 全局
beforeEach:在路由跳转前执行。 - 路由独享
beforeEnter:在进入特定路由前执行。 - 组件内
beforeRouteEnter:在进入组件前执行(如果目标路由有组件)。 - 全局
beforeResolve:在导航被确认前执行。 - 全局
afterEach:在导航完成后执行。
- 全局
6.3 组件内守卫
组件内守卫是定义在 Vue 组件内部的守卫,允许你在组件级别控制路由导航。组件内守卫提供了更细粒度的控制,适用于特定组件的逻辑(如数据加载、权限验证、离开确认等)。Vue Router 4.x.x 提供了以下三种组件内守卫(也是执行顺序):
beforeRouteEnter:在进入组件前执行。beforeRouteUpdate:在当前路由改变但组件复用时执行。beforeRouteLeave:在离开当前路由前执行。
6.3.1 beforeRouteEnter
作用:在进入组件前执行,此时组件实例尚未创建。
参数:
to:目标路由对象(RouteLocationNormalized),包含目标路由的信息(如路径、参数、查询等)。from:当前路由对象(RouteLocationNormalized),包含当前路由的信息。
返回值:
false:取消当前导航。RouteLocationRaw(如路径字符串或路由对象):重定向到指定路由。undefined或true:继续当前导航。
访问组件实例:由于组件实例尚未创建,无法直接访问
this,但可以通过next回调函数访问。示例:
export default { beforeRouteEnter(to, from, next) { next(vm => { // 通过 `vm` 访问组件实例 vm.loadData(); // 加载数据 }); } };
6.3.2 beforeRouteUpdate
作用:在当前路由改变但组件复用时执行(如动态路由参数变化)。
参数:
to:目标路由对象(RouteLocationNormalized)。from:当前路由对象(RouteLocationNormalized)。
返回值:
false:取消当前导航。RouteLocationRaw:重定向到指定路由。undefined或true:继续当前导航。
访问组件实例:可以直接访问
this。示例:
export default { beforeRouteUpdate(to, from) { this.fetchData(to.params.id); // 根据新参数加载数据 } };
6.3.3 beforeRouteLeave
作用:在离开当前路由前执行,通常用于防止用户误操作(如未保存表单)。
参数:
to:目标路由对象(RouteLocationNormalized)。from:当前路由对象(RouteLocationNormalized)。
返回值:
false:取消当前导航。RouteLocationRaw:重定向到指定路由。undefined或true:继续当前导航。
访问组件实例:可以直接访问
this。示例:
export default { beforeRouteLeave(to, from) { if (this.isFormDirty) { const confirmLeave = confirm('您有未保存的更改,确定离开吗?'); if (!confirmLeave) { return false; // 取消导航 } } // 继续导航 } };
6.4 完整的导航解析流程
- 导航被触发。
- 在失活的组件里调用
beforeRouteLeave守卫。 - 调用全局的
beforeEach守卫。 - 在重用的组件里调用
beforeRouteUpdate守卫(2.2+)。 - 在路由配置里调用
beforeEnter。 - 解析异步路由组件。
- 在被激活的组件里调用
beforeRouteEnter。 - 调用全局的
beforeResolve守卫(2.5+)。 - 导航被确认。
- 调用全局的
afterEach钩子。 - 触发 DOM 更新。
- 调用
beforeRouteEnter守卫中传给next的回调函数,创建好的组件实例会作为回调函数的参数传入。
